- +94 112 883 318
- info@ncdalliancelanka.org
- Mon - Fri: 8.00am - 4.00pm Sat: 8.00am - 12.00pm
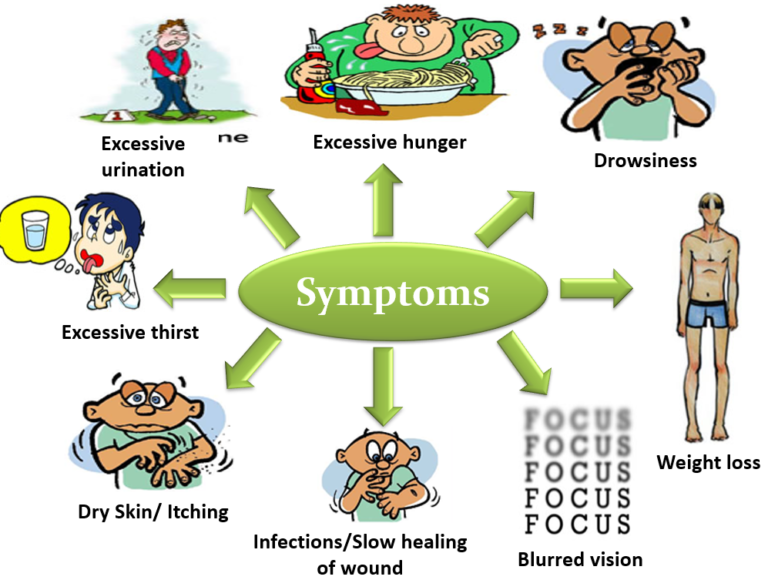
Diabetes is a disorder where the body does not produce insulin or it is inadequate to be used effectively. There are three types of diabetes types :
Gestational diabetes mellitus [diabetes in pregnancy].
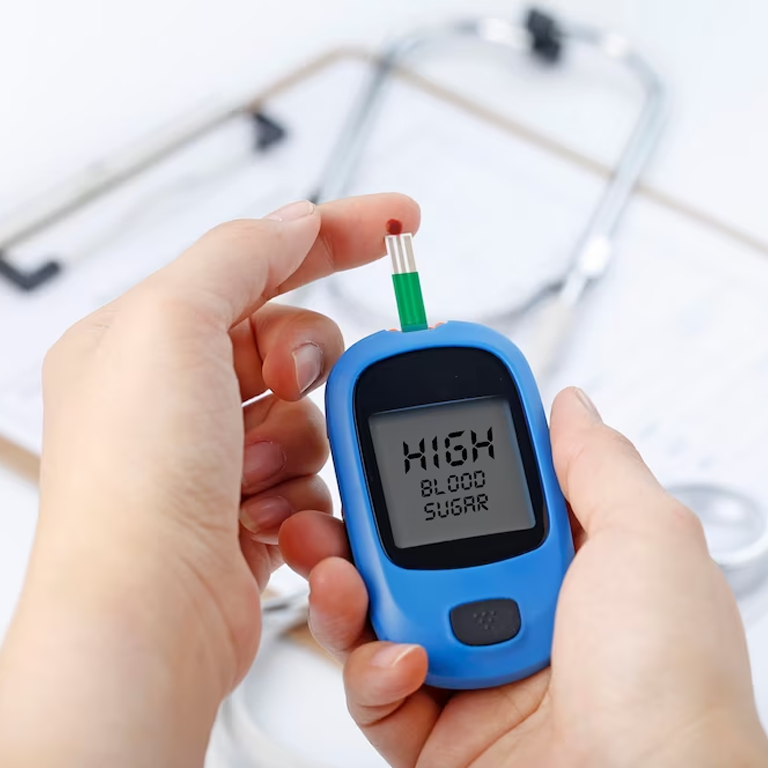
Diabetes can be detected using the following biochemical parameters;
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes can be detected using the following biochemical parameters;
Fasting Blood Glucose > 100-125 mg/ dL and
2 hour OGTT value is > 140-199 mg/dL
HbA1c > 5.7%
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus develops in childhood and adolescence when the pancreas does not produce insulin. It requires lifelong insulin therapy for survival.
The most common type is type 2 diabetes, which occurs usually in adults, but no age is exempt. The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t make enough insulin.
Gestational Diabetes is a form of diabetes consisting of high blood glucose levels during pregnancy. It usually appears around 28th week and disappears after pregnancy. However, it increases the risk of developing T2D in later life in both mother and child.