- +94 112 883 318
- info@ncdalliancelanka.org
- Mon - Fri: 8.00am - 4.00pm Sat: 8.00am - 12.00pm
Heart attacks and strokes happen when blood flow is blocked to the heart and the brain due to a blockage or a build-up of fatty deposits on the inner walls of the blood vessels that supply the heart or brain. Strokes can be caused by bleeding from a blood vessel in the brain or from blood clots.

CVDs are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels.
They include;
• Hypertension
• Coronary heart disease – a disease of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle
• Cerebrovascular disease – a disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain
• Peripheral arterial disease – a disease of blood vessels supplying the arms and legs

Hypertension is high blood pressure. Blood pressure is created by the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels (arteries) as it is pumped by the heart. The higher the pressure, the harder the heart has to pump. If your Blood Pressure is consistently above normal, it may result in a diagnosis of high blood pressure or hypertension.
Normal blood pressure measures are;
Systolic – <140 mmHg
Diastolic -<90 mmHg
Systolic is the pressure developed when heart is contracting. Diastolic is the pressure inside the heart when it is relaxing. If the blood pressure is higher than 140/90 mmHg is taken as hypertension. Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, Myocardial Infarction(MI), Peripheral vascular disease, and chronic kidney disease.
Hypertension is called a “silent killer”. Most people with hypertension are unaware of the problem because it may have no warning signs or symptoms. For this reason, blood pressure must be measured regularly.
Following are the common symptoms of hypertension;
• Chest pain/ angina.
• Heart attack
• Heart failure
• An irregular heartbeat can lead to sudden death.
• Stroke
• Kidney damage, leading to kidney failure

It is important to detect CVD early so that prevention through lifestyle counseling and medication can prevent complications leading to morbidity and mortality.
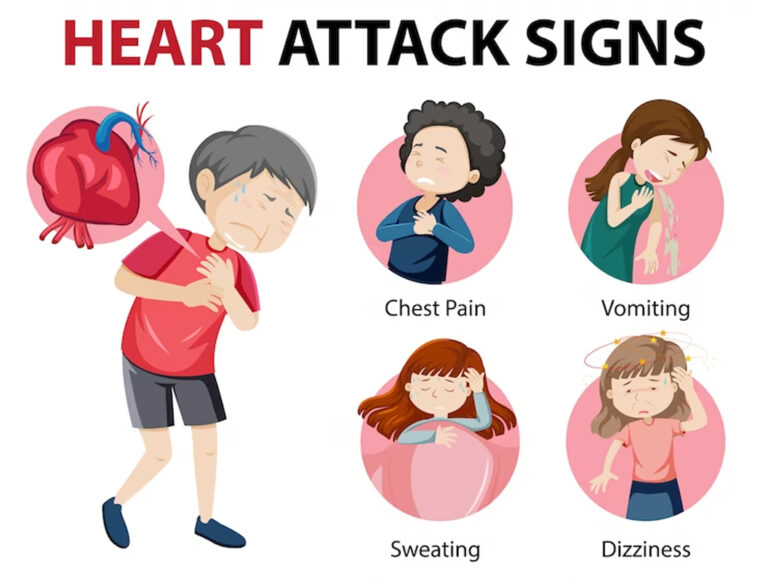
Signs of heart attack;

A heart attack may occur if a blood clot is stuck in a blood vessel that goes to the heart.
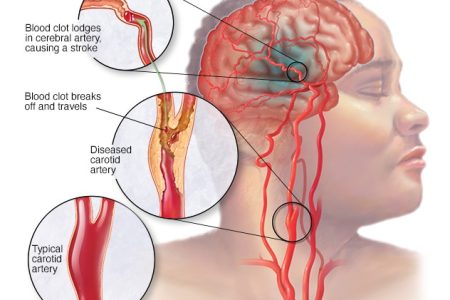
A stroke occures when the arteries to the brain are narrowed/ blocked or rupture. A stroke is a medical emergency — brain tissue begins to die within` few minutes of a stroke.
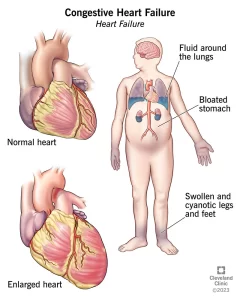
The most common complications of heart disease. Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet body requirements.
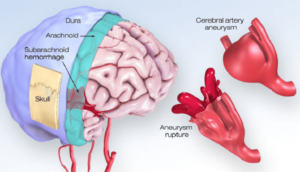
An aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of an artery. If an aneurysm bursts, you may have life-threatening internal bleeding.

Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency. It is the sudden loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness due to a problem with the heart’s electrical system. If not treated immediately, it results in sudden death.
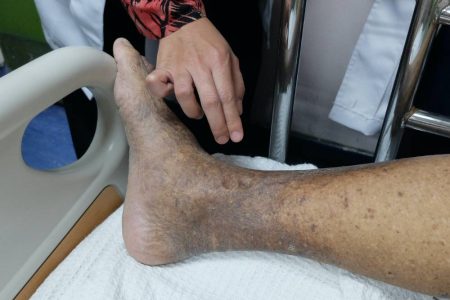
In this condition, the arms or legs — usually the legs — don’t get enough blood. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (Intermittent claudication). Atherosclerosis can lead to peripheral artery disease.